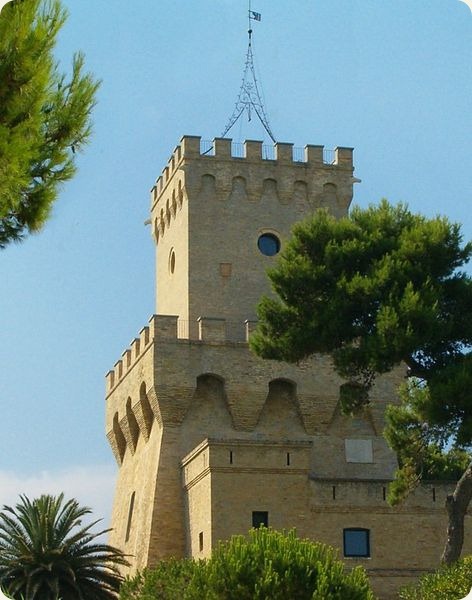
Lazio is one of the 20 administrative regions of Italy, situated in the central/southern peninsular section of the country. With about 5.7 million residents and a GDP of more than 170 billion euros, Lazio is the third most populated and the second richest region of Italy. It includes Rome, capital and largest city of Italy.
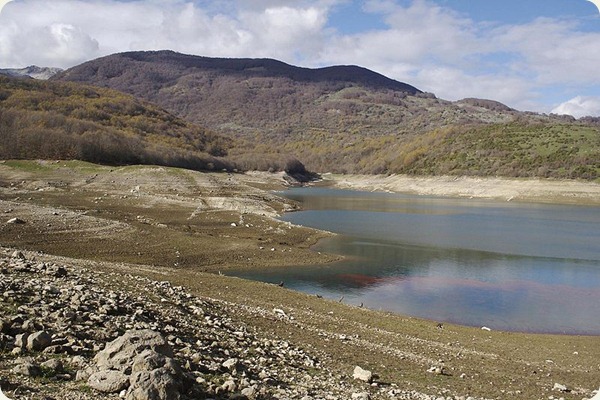
Lazio is one of the 20 administrative regions of Italy, situated in the central/southern peninsular section of the country. With about 5.7 million residents and a GDP of more than 170 billion euros, Lazio is the third most populated and the second richest region of Italy. It includes Rome, capital and largest city of Italy.The coast of Lazio is mainly composed of sandy beaches, punctuated by the headlands of Circeo (541 m) and Gaeta (171 m). The Pontine Islands, which are part of Lazio, lie opposite the southern coast. Behind the coastal strip, to the north, lies the Maremma Laziale (the continuation of Tuscan Maremma), a costal plain interrupted at Civitavecchia by the Tolfa Mountains (616 m). The central section of the region is occupied by the Roman Campagna, a vast alluvial plain surrounding the city of Rome, with an area of approximately 2,100 km2 (811 sq mi). The southern districts are characterized by the flatlands of Agro Pontino, a once swampy and malarial area, that was reclaimed over the centuries.

The Preapennines of Latium, marked by the Tiber valley and the Liri with the Sacco tributary, include on the right of the Tiber, three groups of mountains of volcanic origin: the Volsini, Cimini and Sabatini, whose largest former craters are occupied by the Bolsena, Vico and Bracciano lakes.
To the south of the Tiber, other mountain groups form part of the Preapennines: the Alban Hills, also of volcanic origin, and the calcareous Lepini, Ausoni and Aurunci Mountains.
The Apennines of Latium are a continuation of the Apennines of Abruzzo: the Reatini Mountains with Terminillo (2,213 m), Mounts Sabini, Prenestini, Simbruini and Ernici which continue east of the Liri into the Mainarde Mountains. The highest peak is Mount Gorzano (2,458 m) on the border with Abruzzo.
With a population of about 5.7 million, Lazio is the third most populated region of Italy. The overall population density in the region is 332 inhabitants per km2. However, the population density widely ranges from almost 800 inhabitants per km2 in the highly urbanized Province of Rome to less than 60 inhabitants per km2 in the mountainous and rural Province of Rieti. As of January 2010, the Italian national institute of statistics ISTAT estimated that 497,940 foreign-born immigrants live in Lazio, equal to 8.8% of the total regional population.
source: Immagini d’Italia

Custom Search
If you liked this article, subscribe to the feed by clicking the image below to keep informed about new contents of the blog: